List
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
List
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
String item = iterator.next();
if("B".equals(item)) {
list.remove(item); // 这里会抛出ConcurrentModificationException
}
}
// 这两种写法在性能上没有本质区别 for (String item : list) {
System.out.println(item);
}
Iterator
String item = iterator.next();
System.out.println(item);
}
public class TreeNode {
String value;
List<TreeNode> children;
// 构造方法等省略
}
public class TreeIterator implements Iterator
private Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
public TreeIterator(TreeNode root) {
if (root != null) {
stack.push(root);
}
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return !stack.isEmpty();
}
@Override
public TreeNode next() {
if (!hasNext()) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
TreeNode current = stack.pop();
// 将子节点逆序压栈,保证遍历顺序正确
for (int i = current.children.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
stack.push(current.children.get(i));
}
return current;
}
}
public class ChunkedProductIterator implements Iterator
private final ProductService productService;
private Iterator<Product> currentChunk;
private int currentPage = 0;
private final int chunkSize = 1000;
public ChunkedProductIterator(ProductService productService) {
this.productService = productService;
loadNextChunk();
}
private void loadNextChunk() {
List<Product> chunk = productService.getProductsByPage(currentPage, chunkSize);
currentChunk = chunk.iterator();
currentPage++;
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
if (currentChunk.hasNext()) {
return true;
}
// 尝试加载下一块
loadNextChunk();
return currentChunk.hasNext();
}
@Override
public Product next() {
if (!hasNext()) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
return currentChunk.next();
}
}
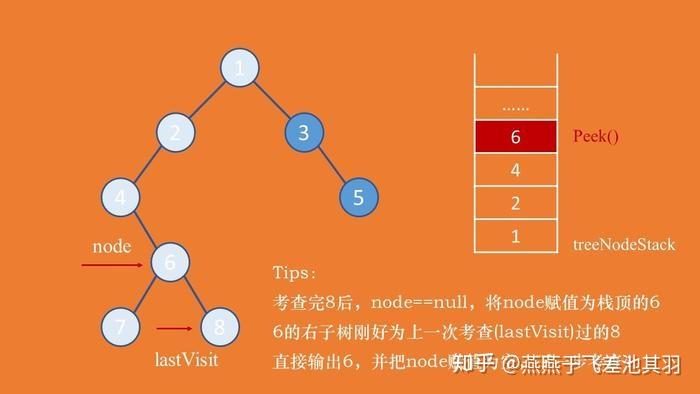
你可能想看: